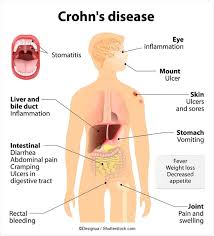
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that primarily affects the digestive tract. It is characterized by inflammation and damage to the gastrointestinal tract, often occurring in patches and affecting any part of the digestive system from the mouth to the anus. Crohn’s disease is one of the two main types of IBD, with the other being ulcerative colitis.
Key features of Crohn’s disease include:
- Inflammation: The inflammation associated with Crohn’s disease can affect multiple layers of the intestinal wall, leading to various symptoms and complications. This inflammation can occur in patches, with healthy tissue in between.
- Common Symptoms: The most common symptoms of Crohn’s disease include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and malnutrition. The severity and specific symptoms can vary widely among individuals. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, refer to a Best Gastroenterologist in Lahore.
- Extraintestinal Manifestations: Crohn’s disease is not limited to the digestive tract. It can also result in extraintestinal complications, such as joint pain, skin rashes, eye problems, and liver conditions.
- Complications: Over time, Crohn’s disease can lead to complications like strictures (narrowing of the intestines), fistulas (abnormal connections between different parts of the intestine or other organs), abscesses, and an increased risk of colon cancer.
- Cause: The exact cause of Crohn’s disease is not well understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Family history of IBD can increase the risk.
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, imaging studies (e.g., CT scans, MRIs), and endoscopic procedures (e.g., colonoscopy and upper endoscopy) to visualize the gastrointestinal tract and take tissue samples for evaluation.
Treatment:
The management of Crohn’s disease aims to control inflammation, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Treatment may include medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, biologics, and antibiotics. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the intestine or address complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Individuals with Crohn’s disease often need to make dietary and lifestyle changes to manage their condition. These changes may include avoiding trigger foods, maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting regular exercise.
- Ongoing Care: Crohn’s disease is a chronic condition that requires long-term management. Patients work closely with healthcare providers, including gastroenterologists and dietitians, to develop a personalized treatment plan and regularly monitor their condition.
It’s important to note that Crohn’s disease is a highly individualized condition, and the severity and course of the disease can vary greatly from one person to another. While there is no cure for Crohn’s disease, with appropriate medical care and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with the condition can lead fulfilling lives and manage their symptoms effectively. To know more, visit a Best Gastroenterologist in Rawalpindi.
